Humanoid Robot
Torobo
Torobo has the following characteristics and can be used for machine learning research or to automate tasks that involve active contact with objects or the environment.
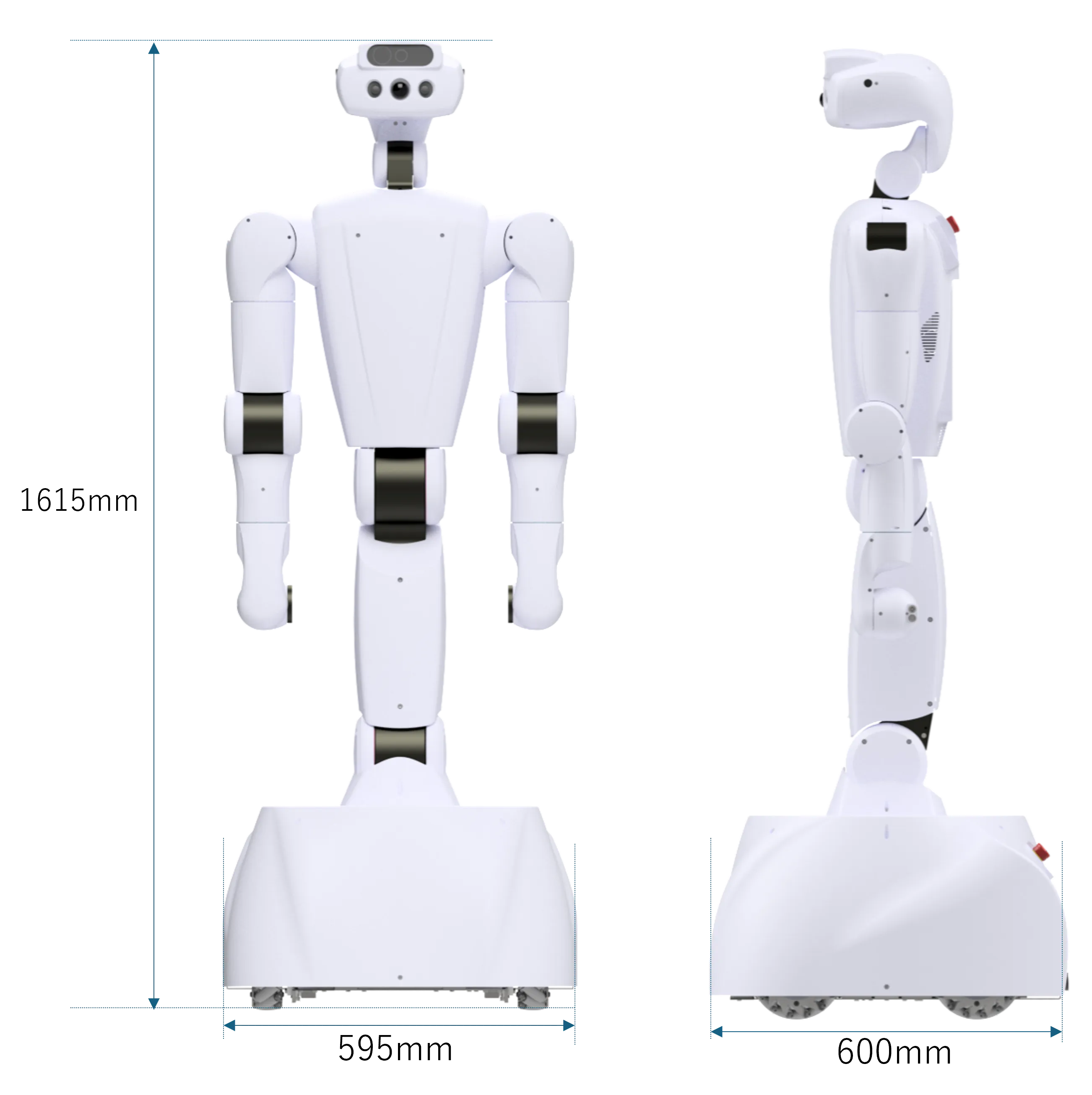
Size and Strength Equivalent to Humans
With a height of 1615 mm and a cart width of 590 mm, the size of the robot is close to that of a human. The payload of one arm is 7 kg at the worst-case holding posture, which are sufficient to conduct robotics R&Ds to replace human work.
Joint Configurations that Enable a Wide Variety of Tasks
The joint configuration of 7-axis dual arms, 3-axis waist (pitch, pitch, yaw), 3-axis neck (yaw, pitch, roll), and 4-axis undercarriage (omni-directional mobile base) enables the robot to do tasks with a range of motion similar to human beings in living and working spaces of people.
Torque Sensing and Impedance Control of the Arm and Waist
Equipped with torque sensors at all joints of the arms and waist, the joint torque control enables safe contact stops and force-controlling task executions. Assembly tasks, cooking, and physical interaction with humans can be performed more safely and skillfully.
ROS Support
Since it is ROS-compatible, the robot in Gazebo (a simulator for ROS) and the actual robot can be operated using the same program. This makes it possible to safely verify the robot's behavior. In addition, trajectory planning and self-interference detection using the MoveIt! are implemented as a standard.
Basic Performance
This video shows the basic performance of Torobo. *Direct teaching after 2:20 is for in-house research and is not included in the basic package.※The videos are from the old Torobo and not from the current Torobo.
Piching Ball
Torobo is lighter than the older version, enabling faster motion such as throwing a ball.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Sensors (optional head) |
Wide-angle stereo camera x 1 Fisheye camera x 1 Depth camera x 1 Stereo microphone x 1 |
| Effectors (optinal head) | Speaker x 1 |
| Height | 1615 mm |
| Weight | approx. 120 kg |
| Payload |
Worst posture: 7 kg (single arm) |
| External terminals (back of the robot) |
Digital input x 8 Digital output x 8 Analog input: x 8 Analog output x 8 Ethernet x 2 |
| Tool flange (tip of the arm) |
24V DC power supply terminal x 1 General-purpose signal wire x 8 |
| Onboard computer(optional) | A single PC is standardly equipped and is used for controlling the robot. Additionally, it is possible to install a second optional PC with Nvidia RTX 4070. The second PC is used for controlling the sensors in the head. |
| Head(optional) | Head is optionl part. you can choose the head from 2 types. |
| End-effector(optional) | End-effector is optionl part. you can choose the end-effector from hand or gripper. |
| Power source | Built-in battery (continuous operation while charging is also possible) |
| Battery continuous operation time | Up to approx. 3 hours |
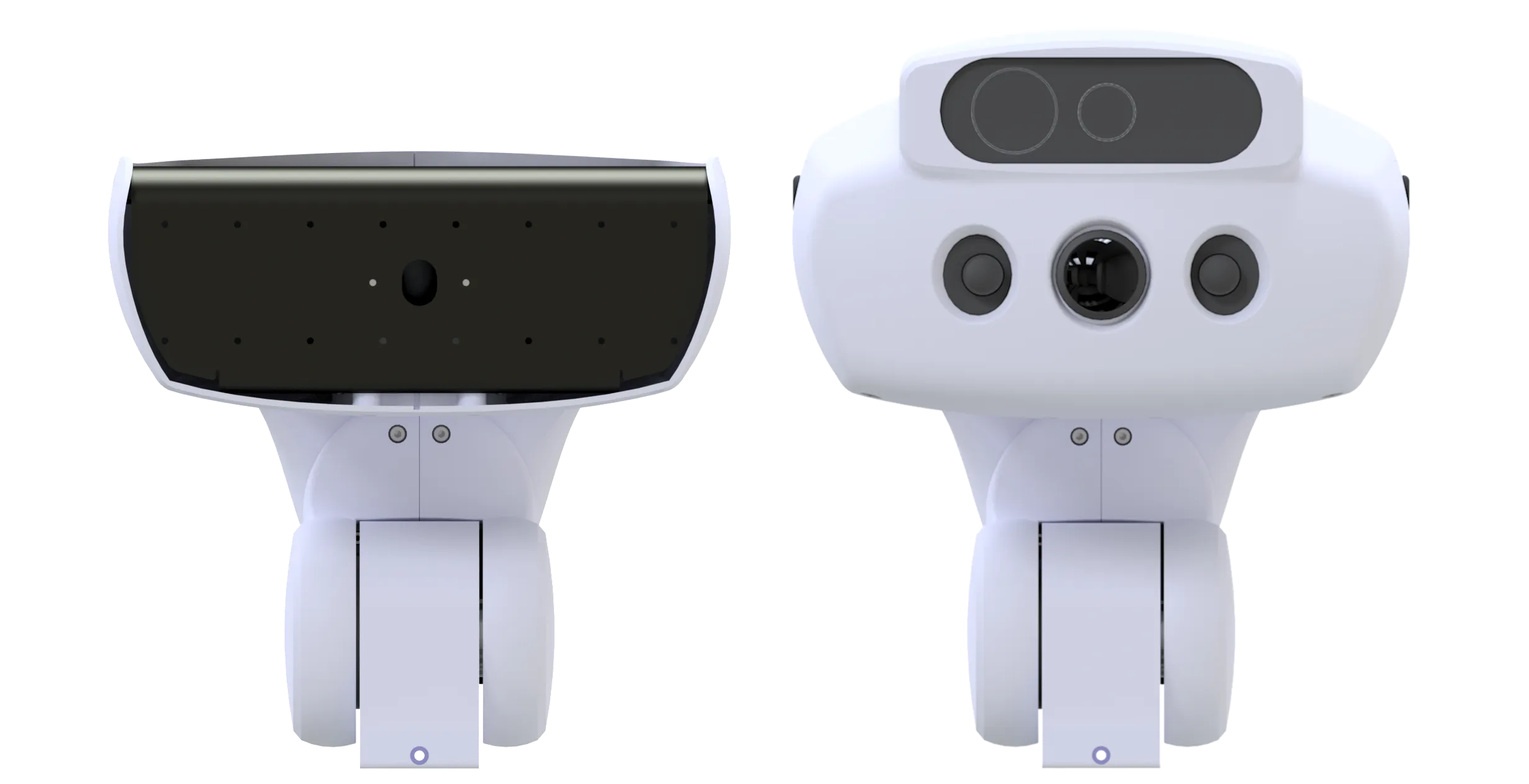
Head (option)
The head is optional and can be chosen from two types. The first type is a version without any sensors, which serves as the default version. The second type is equipped with several sensors and output devices. The sensors include a ToF-based depth camera, a fisheye camera, a wide-angle stereo camera, and microphones. Each camera can capture RGB images. Additionally, a speaker is installed as an output device. For more detailed information, please contact us via our email address.
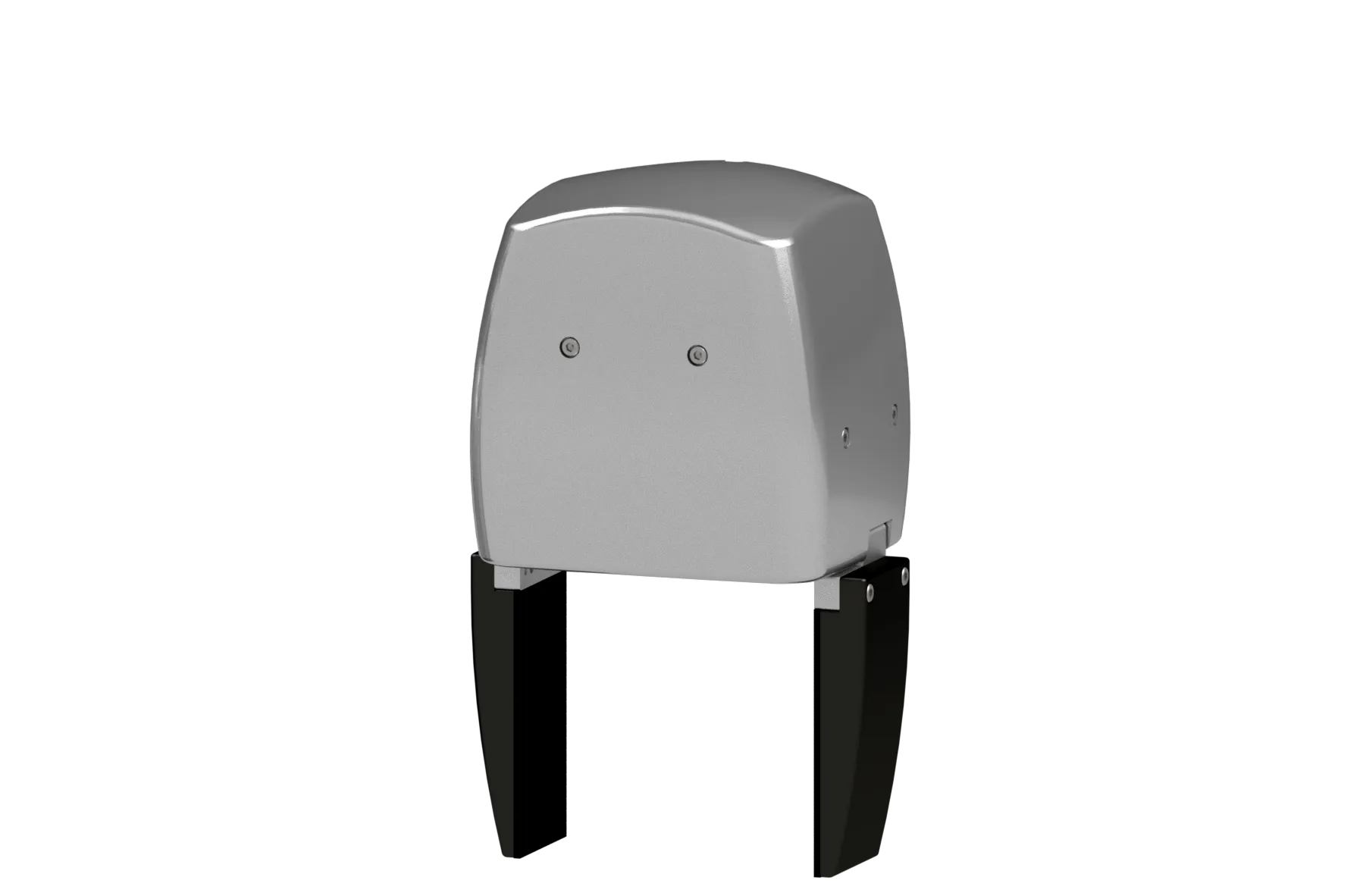
End-Effector (option)
end-effector is optionl part. you can choose the endeffector from gripper. The gripper is an in-house product featuring controllable gripping force via current limitation and back-drivable functionality. For further details, please contact us via our email address.

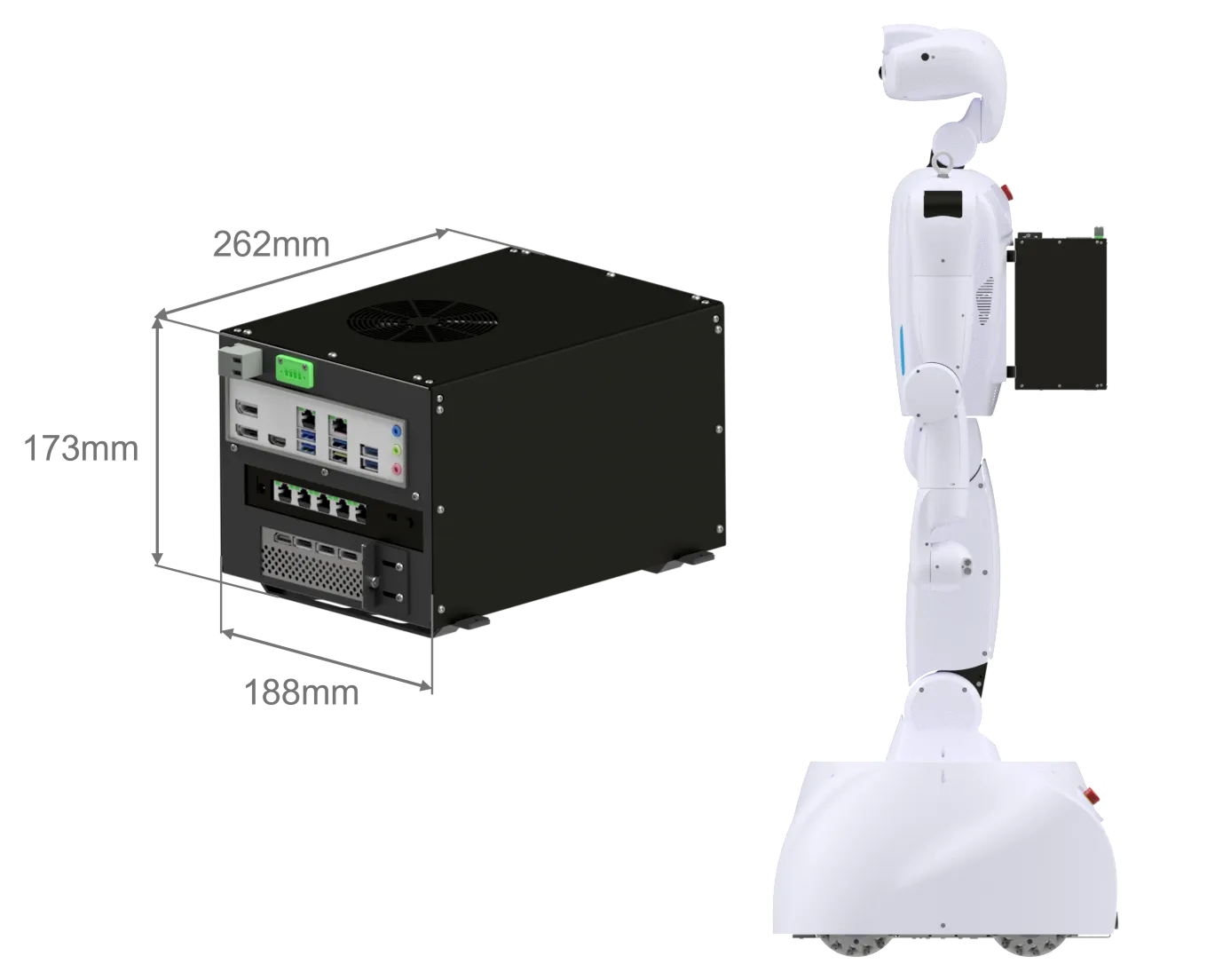
PC for Image Processing (option)
The image processing PC is responsible for controlling the sensors mounted in the head. Equipped with an Nvidia RTX 5070, this PC can perform training and inference of machine learning models. For more detailed information, please contact us via our email address.
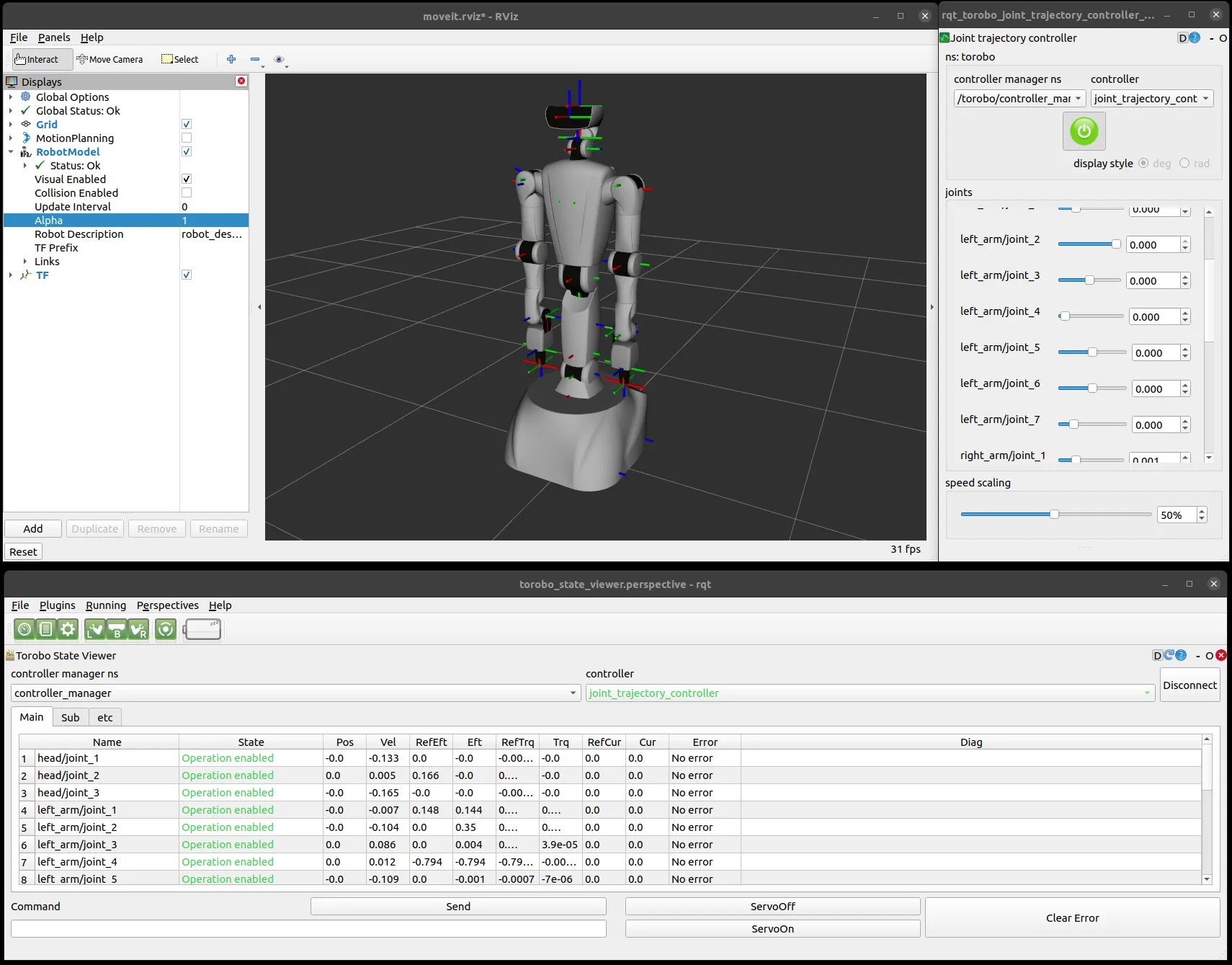
Software
The basic functions required to move a force-controllable humanoid robot are implemented. Torobo can utilize impedance control in a Cartesian coordinate system, fall prevention by monitoring ZMP, a state machine for connecting multiple movements, and safety stop based on interference detection. Torobo's software is based on ROS. Therefore, in addition to the easy use of the above functions, state visualization with RViz, trajectory planning using a ROS standard software MoveIt!, and logging and saving of the robot's sensor information (camera images, joint angles, joint torques, etc.) are available.
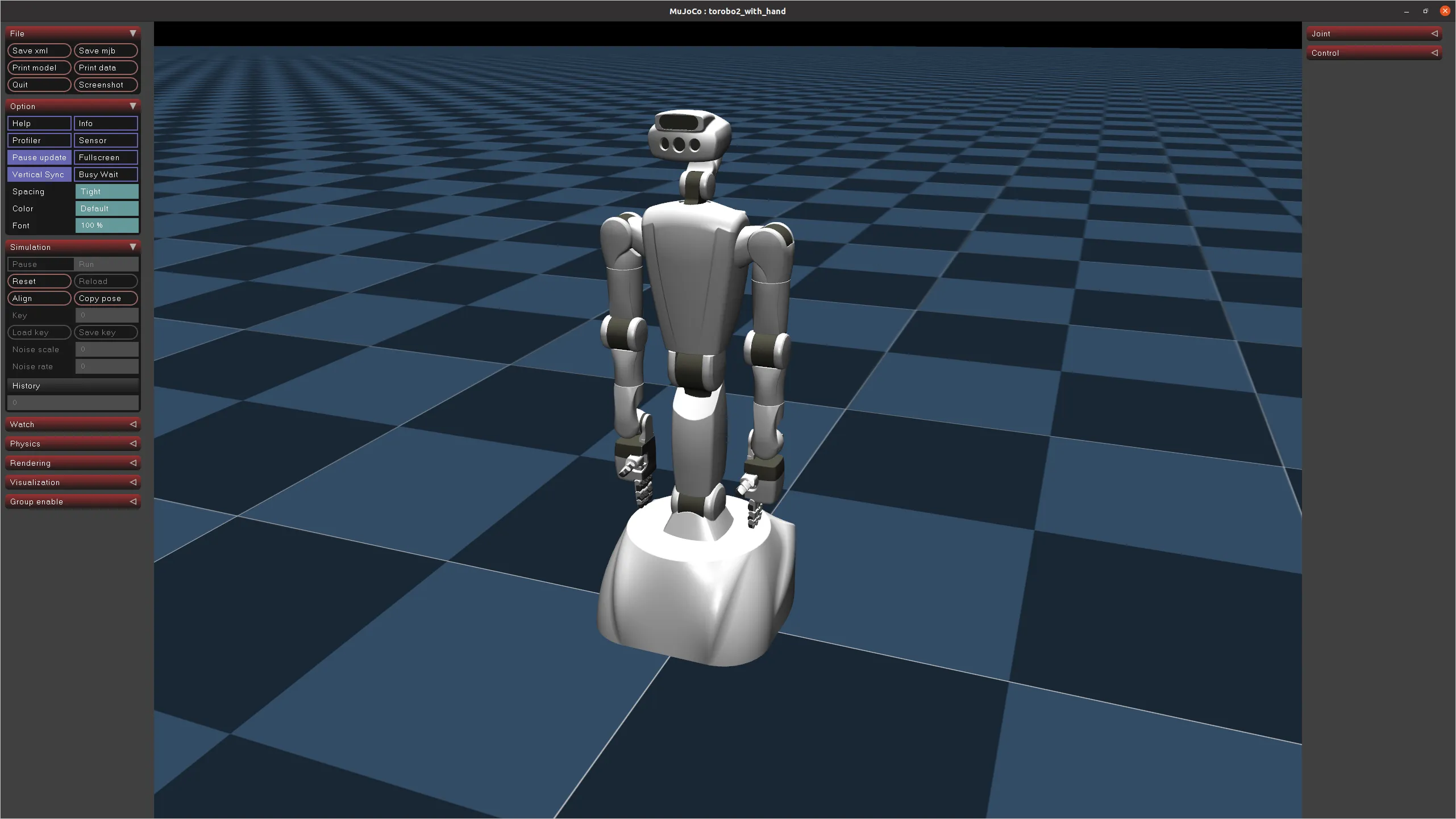
Simulation Model in MuJoCo
The model can be tested in MuJoCo made by Google DeepMind. For detailed usage instructions, please refer to our company blog or GitHub repository.
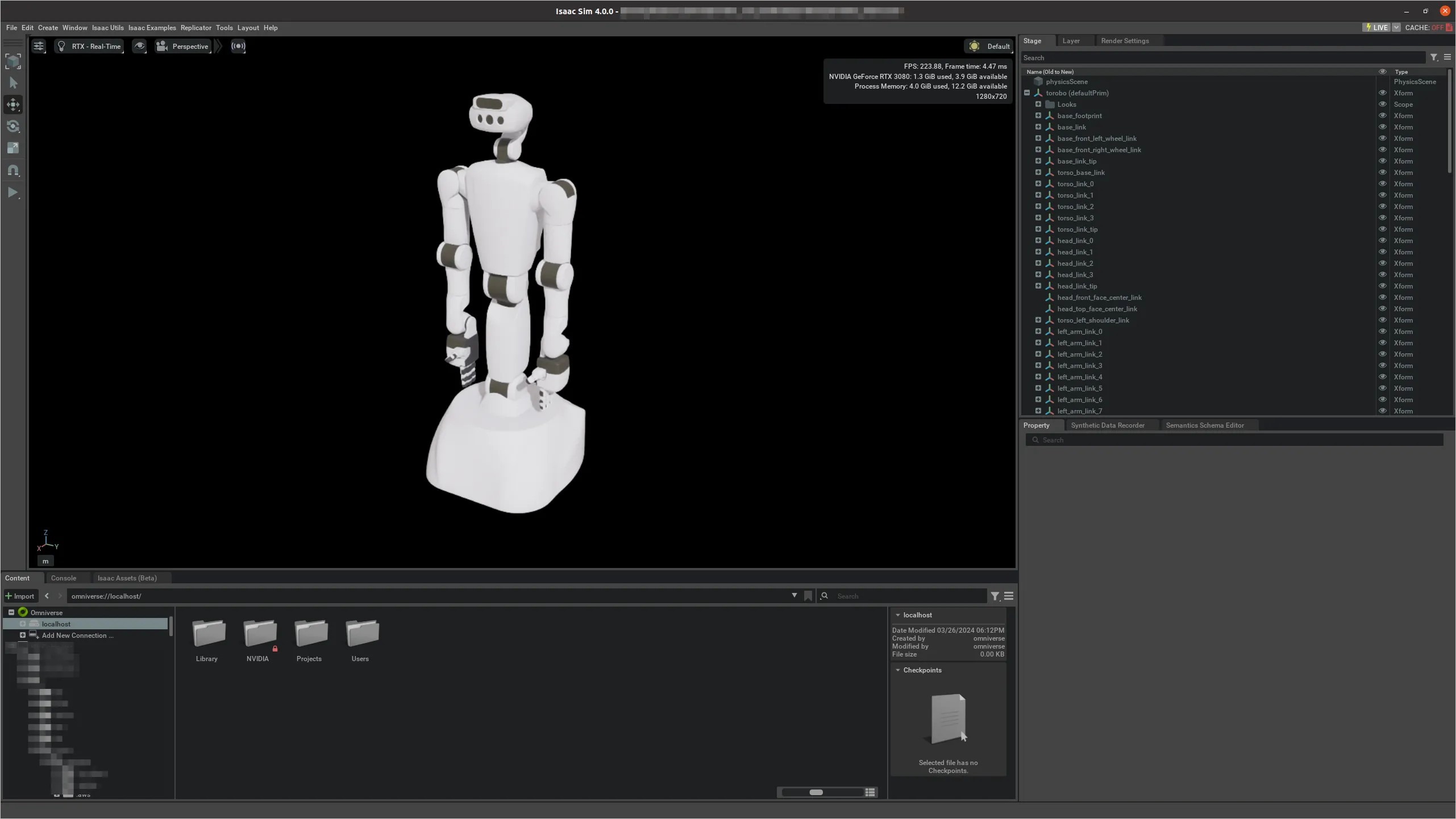
Simulation Model in Isaac Sim
The model can be tested in Isaac Sim made by NVIDIA. For detailed usage instructions, please refer to our company blog or GitHub repository.